Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Spermiation, Sperm, Oogenesis, Oogonia, Primary Oocytes, Secondary Oocyte, Zona Pellucida, Menstrual Cycle, Menopause, Ovulation, Menstrual Phase, Follicular Phase, Luteal Phase, Implantation, etc.
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction
The embryonic structure that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female is
Which of the following hormones play important role in menstrual cycle?
Where is acrosome present in human?
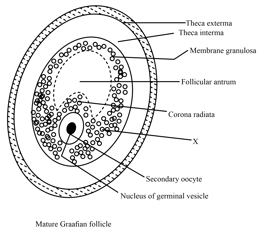
Choose the correct option to label the region .
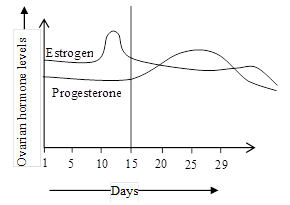
Read the graph given below and identify the period of follicular phase:
An organism's life history largely concern its lifetime growth and reproduction. For example, why is it that some plants - especially those we regard as weeds - produce vast number of tiny seeds while some trees produce, fewer, bigger seeds? Why do some species breed once in their lifetime in one big burst while other breed repeatedly and at more moderate level?
i) What is the opinion of ecologists for this life history variation among organisms?
Mammalian sperm cells are highly specialized male gametes produced only for the function of fertilization. During spermatogenesis, these cells lose several subcellular entities and retain only those which are absolutely essential. Therefore, the mature sperm cells from humans will contain
The deletion of a segment of mitochondrial DNA, specifically in the mature sperm of Mr. led to infertility. This deletion results in the lack of a mitochondrial transport protein critical for ATP production. Mr. was referred to an Assisted Reproduction Centre for several remedial possibilities. Based on this information, the correct option is
Clear cut distinction between vegetative, reproductive and senescent phase is shown by
In all the sexually reproducing organisms, events involved are
The end of juvenile phase marks the beginning of:
The time period from fertilisation to childbirth is known as the _____ (gestation period/parturition).
Name the hormone released during parturition.
Choose the correct option:
| Column I | Column II |
| (A) Head | (i) Enzymes |
| (B) Middle piece | (ii) Sperm motility |
| (C) Acrosome | (iii) Energy |
| (D)Tail | (iv) Genetic material |
Assertion (A): In a woman after hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), the ovarian cycle is stopped.
Reason (R): Stoppage of FSH secretion.
In human females, when does oogenesis begin?
Which of the following antibodies is present abundantly in the colostrum secreted during the initial days of human lactation?
The term 'clone' cannot be applied to offspring formed by sexual reproduction because
Which one of the following does NOT represent asexual reproduction?
